Design & Technology
Key Stage 3 Design Technology
Curriculum Intent and Overview
The curriculum covers a wide range of opportunities which run alongside a rich extra-curricular timetable. This includes both creative and STEM elements. Students are extremely proud of their achievements, and they really value the supportive nature and encouragement the department gives them. The curriculum develops and promotes:
- A love for creativity and design.
- Critical and lateral thinking, and problem solving.
- Independent learning, and transferable skills.
The Department
Curriculum Leader: Mrs C Draper
What will be studied?
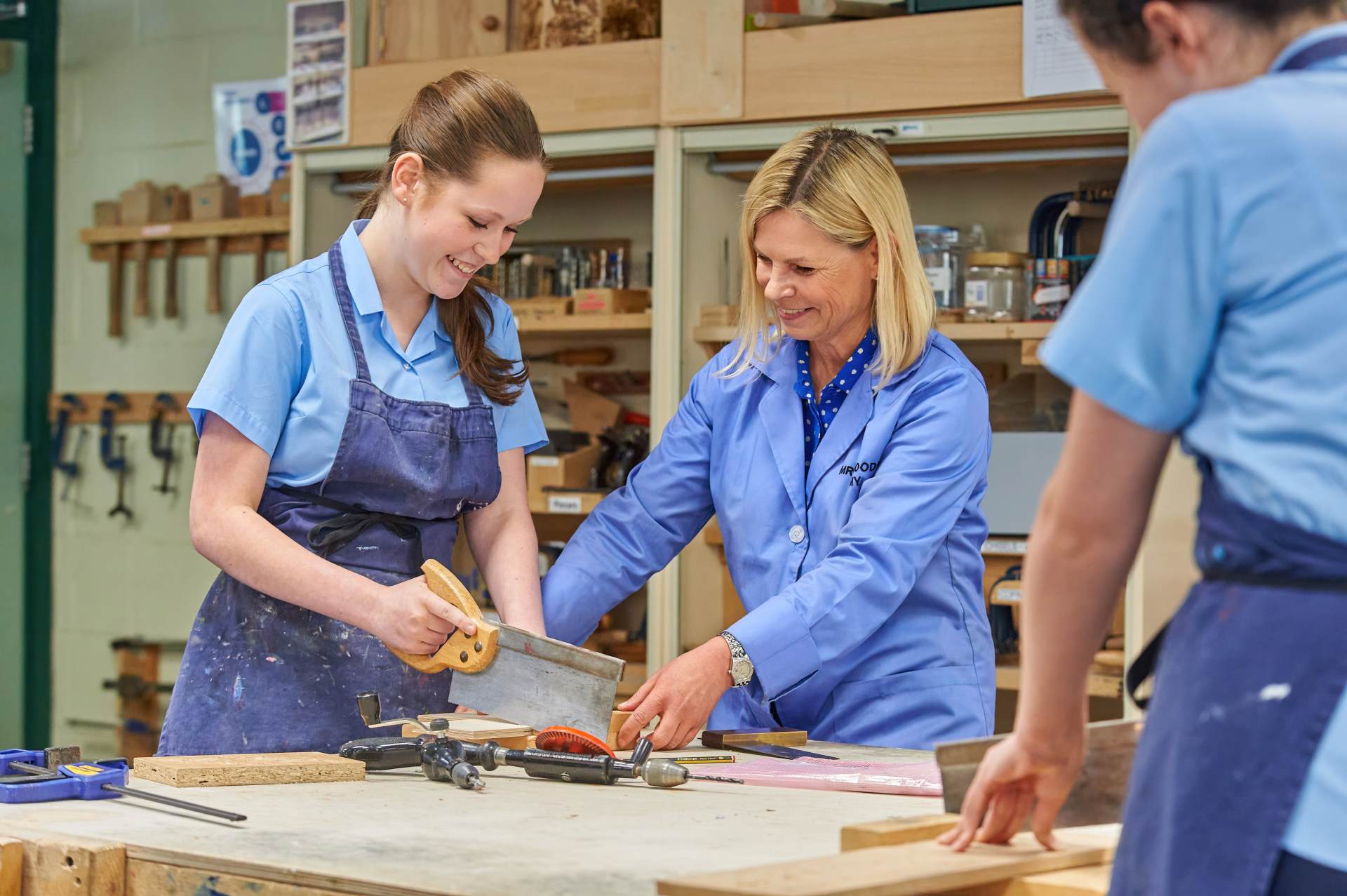 Within Design and Technology students in Years 7, 8 and 9 study Food and Textiles and Design & Technology on a rotation system, where they complete one project per topic each year.
Within Design and Technology students in Years 7, 8 and 9 study Food and Textiles and Design & Technology on a rotation system, where they complete one project per topic each year.
Students have access to specialised textiles rooms where new techniques are taught and applied via a range of projects which include dying techniques, machine sewing, decorative embellishment techniques, construction and pattern making.
Food Science and Nutrition is taught in our food rooms where students learn about a variety of cultural dishes, and the science behind our food. These lessons are very popular, and students enjoy taking home their creations to share with their family after a practical lesson.
Design Technology is taught in specialised workshops and students learn a variety of woodwork and metal work techniques – the use of plastics within design, electronics and circuit boards are also included within topic content.
New technologies and STEAM are an important part of our curriculum, and we use state of the art equipment including CAD/CAM (Computer Aided Design/Computer Aided Manufacture). Product Design is offered at GCSE where students can opt to take a resistant materials or textiles focus, enabling progressing into the engineering and design industries.
What support is needed?
- Encouragement in creativity, and promotion of the importance of STEAM, and the importance of getting girls in Engineering.
- Museums e.g. Science Museum and the Design Museum.
How will they be assessed?
Assessment is carried out via extended projects which are set and marked by teachers. These projects are designed to allow students to demonstrate their knowledge and technical ability in Art. Targets are set for students during the year and progress towards those targets are monitored by frequent discussions with students and by written feedback.
Key Stage 4 Design Technology
Curriculum Intent and Overview
The curriculum covers a wide range of opportunities which run alongside a rich extra-curricular timetable. This includes both creative and STEM elements. Students are extremely proud of their achievements, and they really value the supportive nature and encouragement the department gives them. The curriculum develops and promotes:
- A love for creativity and design
- Critical and lateral thinking, and problem solving
- Independent learning, and transferable skills
GCSE
Exam Board: AQA
Specification Number: 8552
What will be studied?
New technologies and STEAM are an important part of our curriculum, and we use state of the art equipment including CAD/CAM (Computer Aided Design/Computer Aided Manufacture). Design Technology is offered at GCSE where students can opt to take a resistant materials or textiles focus, enabling progressing into the engineering and design industries.
This GCSE Design Technology course will build upon the design-and-make skills used in Years 7-9, developing knowledge and understanding within resistant materials or textiles.
Design Technology is a subject where students gain practical skills that are relevant to everyday life, both at home and at work. They use and develop many key skills, especially communication, numeracy, problem solving and ICT, and become effective independent learners. The coursework is demanding, but the final products and portfolios give most students a sense of real achievement and satisfaction, as well as something to be proud of at home and in future interviews. The new controlled assessment regulations mean that most of the coursework will be done in school, not at home.
Topics covered will include: Knowledge and understanding of properties of materials (paper & card, then at least one of metals, woods, plastics, or smart materials). Skills in the relevant material including use of a range of tools, machines and processes, CAD/CAM, industrial production, different types of drawing and rendering, model making and prototypes, developments (nets), forming (e.g. vacuum forming), packaging, marketing and advertising. Background information such as evolution of product design, product development, environmental issues, human factors, quality control and health and safety.
ICT will be used extensively for desk top publishing, graphics (including drawing, editing digital photos and scanned pictures), spreadsheets and charts, nets, flow charts and CNC work.
Learning Methods
We try to teach as much of the theory as we can through practical work. For example in Year 10 students might be designing and making a storage unit, or textile garment based on a design movement.
Group work, PowerPoint presentations, disassembly and research are other teaching styles used in lessons.
We hope to give students the opportunity to make at least one visit during the course or to hear from a visiting speaker, particularly concerning the industrial applications part of the course, but this is not always possible.
How is the course assessed?
There is one written exam paper of 2 hours carrying 40% of the total marks, including a design question for which you get some prior information and a chance to research before the exam.
60% of the final grade is dependent on a design-and-make project. This will begin in the summer term of Year 10 and will take approximately 45 hours of school time.
In this project students will be given a choice of titles to investigate and then individuals research or recall relevant knowledge and make informed decisions about what is required for a solution. Students have to provide a variety of ideas, plan and carry out the making of a solution and finally test and evaluate the results. The use of ICT in designing, making and presenting your work is very important.
Students will be working individually for most of this time, so they need to show considerable independence and make sure that they meet the deadlines for each part of the project.
What websites are recommended?
BBC Bitesize and AQA for past papers
What equipment is needed?
A calculator, protractor, ruler, pen and pencil and coloured pencils are essential at all times.
A Level Fashion & Textiles
Curriculum Intent and Overview
The curriculum covers a wide range of opportunities which run alongside a rich extra-curricular timetable. This includes both creative and STEM elements. Students are extremely proud of their achievements, and they really value the supportive nature and encouragement the department gives them. The curriculum develops and promotes:
- A love for creativity and design
- Critical and lateral thinking, and problem solving
- Independent learning, and transferable skills
ADT Strategy
Curriculum Leader: Mrs C Draper
Exam Board: AQA
Specification Number: 7562
What will be studied?
We study Fashion and Textiles to develop technical knowledge and practical skills in areas such as drawing, fashion illustration, fabric technology, pattern cutting, computer-aided design (CAD), sewing and garment construction. As well as specific skills invaluable transferable skills will be gained such as increased independence, visual awareness, creative thinking and problem solving, research and analytical skills and presentation skills.
We look back at what iconic products have been made, which designers influenced fashions throughout time, what life events and cultures determined what we wore, what technological advances were made to change what we wear today and what we might wear in the future.
The Fashion and Textile sector is diverse and covers a wide range of roles, from processing raw fibres, such as spinning weaving and dying, to sourcing new materials and products, manufacturing and production, textile technology, marketing branding and retailing, as well as Design.
You will be able to appraise standards and brands of merchandise and will develop the ability to distinguish quality in fabrics.
This creative and thought-provoking qualification gives students the practical skills, theoretical knowledge and confidence to succeed in a number of careers, especially those in the creative industries.
Assessment:
In Year 12 lessons are directed towards broadening experience, skills and knowledge. Students begin their NEA (coursework) towards the end of Year 12 and continue this into most of Year 13.
You will sit 2 exams at the end of Year 13.
Your final grade is made up of:
- 50% exams
- 50% NEA
Expectations of Students:
A passion for fashion and textiles, an intrigue into the history and development of fashion and a desire to explore techniques and processes. Students are expected to take part in personal and group visits to galleries and exhibitions in order to experience fashion and textile work at first hand. Students must commit to additional hours of sketchbook and research preparation per week.
Career Paths:
Most Fashion & Textile courses require a portfolio for entrance from which they can judge the students ability, commitment and potential for themselves. Completion of the A level course will help the students to develop a portfolio of the required standard.
Opportunities for future study and employment cover both academic and artistic fields including fashion designer, retail buyer, retail manager, retail merchandiser, stylist, textile designer, visual merchandiser, illustrator, costume designer, set design, fashion promotion, fashion journalism, makeup artist, jewellery designer, etc.
What websites are recommended?
V&A · The World's Leading Museum Of Art And Design (vam.ac.uk)Home | Fashion and Textile Museum (fashiontextilemuseum.org)PinterestTrend Forecasting & Analytics 2023-2031 | WGSN
What equipment is needed?
A lever arch folder with dividers for the theory element of the course.
Drawing pencils, fineliners, colouring pencils, watercolours and pritt sticks.
Practical resources for Year 12 will mostly be provided by the school and basics will be provided in Year 13. Specific fabrics and connotations would need to be provided by students for their NEA in Year 13.